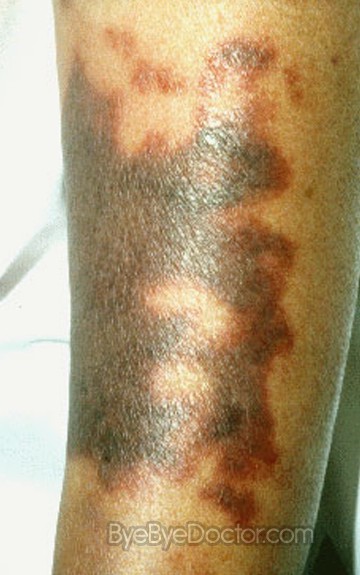
Symptoms
When DIC causes the platelets in the blood as well as the other factors of clotting to become depleted, extreme bleeding or hemorrhage occurs thru out the body. The brutality of this bleeding can go from small red dots and skin bruises to very heavy blood from wounds from surgery or openings of the body, such as nose, mouth, vagina or rectum.
Common symptoms include:
- Bleeding
- Mucosal bleeding
- Cough
- Dyspnea
- Confusion
- Disorientation
- Fever
- Lung damage
- Kidney damage
With DIC organ damage can occur because of extreme blood clotting, which can cause shortness of breath because of damage to lungs, stroke because of damage to the brain, and urine output which is low due to damage with the kidney. In extremely severe cases, low blood pressure can occur with shock as well as very extensive organ failure, can transpire.
In cases of less severe incidents of DIC which is known as chronic DIC, the human body has the ability to recompense for this abnormal clotting. Chronic DIC can create few symptoms, only blood clotting problems which are mild with some minimal bleeding from the mouth or skin.
Causes
There are numerous causes of DIC. This disorder is normally caused by a discharge of chemicals into the blood system from one of the following conditions:
http://www.Symptoms-Causes-treatment.blogspot.com detect diseases at an early stage symptoms, and find out the causes and treatments best suited.
- Blood Poisoning – system-wide infection – especially with gram-negative bacteria
- Labor as well as delivery complications such as: Eclampsia, Amniotic fluid clots and Retained placenta
- Certain cancers
- Extensive tissue injury caused by: Burns and Concussion
- Reaction to blood transfusion
- Shock
- Less common causes include: Prostate surgery complications, Severe head trauma, Venomous snake bites
This condition is associated with many illnesses, particularly in those patients who are very ill like those individuals in an Intensive Care Unit. Stress may also activate clotting factors. DIC is diagnosed with blood tests which are analyzed to count the number of platelets as well as clotting factors. When a patient does have excessive bleeding and he/she is at any risk of DIC, physicians try to act quickly.
There are certain conditions which increase an individual’s chances of developing DIC. While making a diagnosis, the physician will look for any of the following risk factors:
- Recent trauma or injury
- Recent episode of sepsis
- Recent surgery or anesthesia
- Leukemia or any other widespread cancer
- Labor and delivery complications
- Severe liver disease
- Recent reaction to a blood transfusion
Diagnosis
The physician normally makes a diagnosis of DIC based on symptoms as signs, as well as the results of certain specific blood tests. Like the symptoms of DIC, blood levels will very according to how severe is the DIC. The blood will be examined for atypical levels of certain tests, including:
- Platelet count – normally reduced in DIC
- Fibrin degradation products – normally elevated level in DIC
- Fibrinogen – normally reduced in DIC
- Prothrombin time – PT – usually prolonged in DIC
- Partial thromboplastin time – PTT – usually prolonged in DIC
- D-dimer test – normal high level in DIC
- Thrombin test time – usually prolonged in DIC
Treatment
Naturally the goal of treatment is to determine and treat any underlying cause of DIC as well as to treat the problems with clotting itself. Blood clotting factors can be replaced with plasma transfusions. Heparin, a medication used to prevent clotting is often used.
Treatment includes:
- Drug-Heparin sodium
- Surgical treatment limited to treating certain underlying conditions
- Transfusion of blood cells
- Activated Protein C used to control growth of blood clots
- Cornerstone cure of DIC is the alleviation of primary disorder
The treatment or management for DIC is very hard. The use of anticoagulant drugs can be helpful but it can also be extremely hazardous as treatment can also trigger a bleed that an individual cannot convalesce from. Individuals may also receive transfusions of platelets, as well as several other drugs, depending on each individual case.
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Pictures
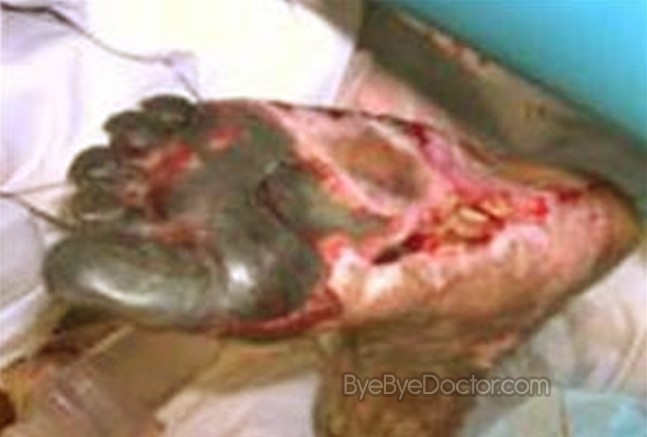
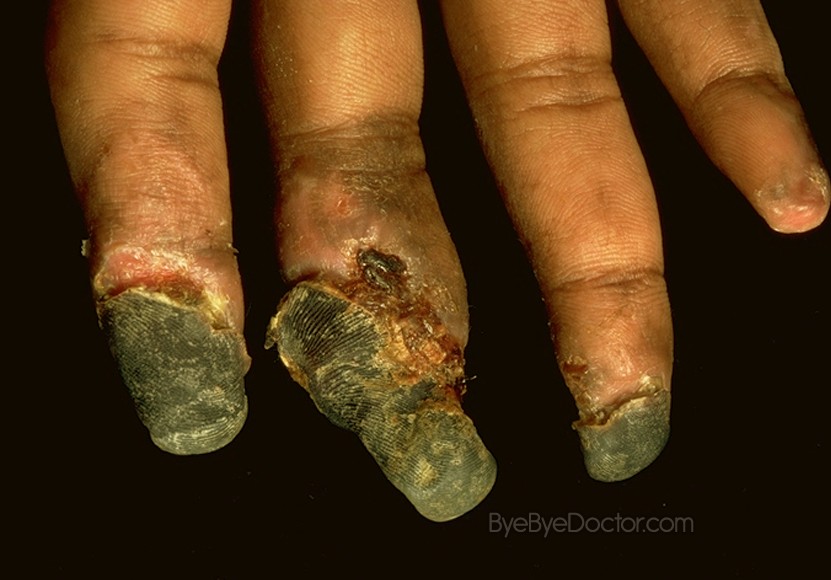
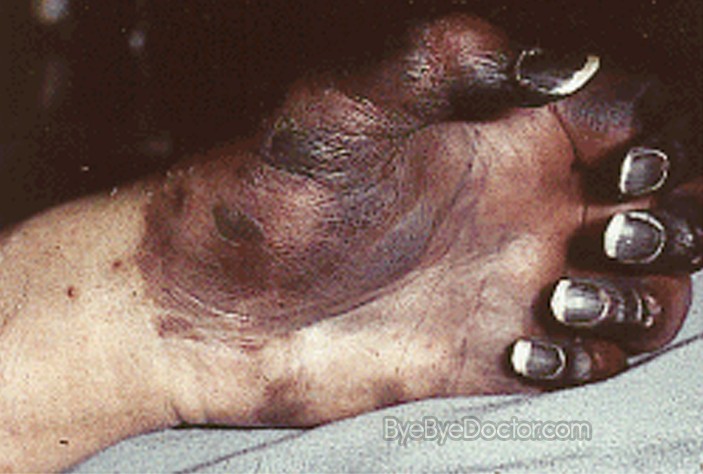
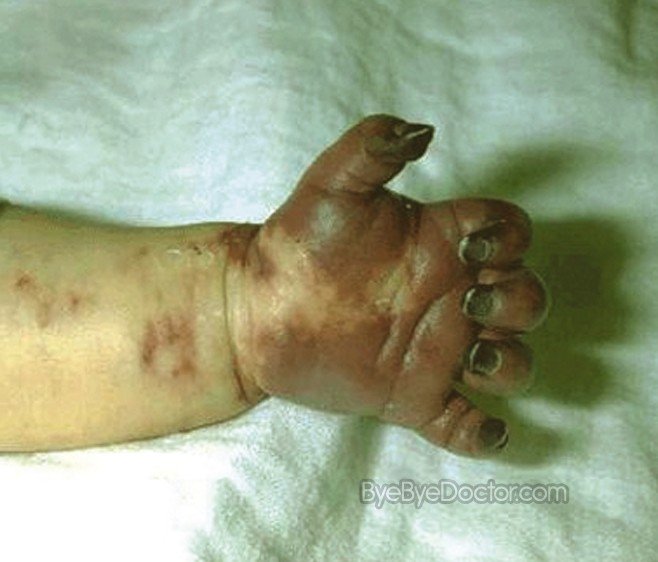 Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation pictures in children
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation pictures in children