Undescended Testicle – Symptoms, Surgery Cost, Causes, Pictures, Treatment
What is an Undescended Testicle?
This is a condition where a testicle has not descended to its correct location in the scrotum or skin bag behind the penis. Testicles normal drop into the correct position before the birth of any baby boy. If there is a problem with testicles being undescended it normally affects only one testicle although there are some cases where both testes can be undescended. This condition is also referred to as cryptorchidism.
A testicle that is undescended is fairly common in baby boys who are born ahead of time or earlier than 37 weeks.
For the majority of boys born with 1 or 2 testicles which are undescended, the problem can correct itself in the first couple of months of life. But if the baby has one that does not correct itself, normally surgery is used to rearrange the testicle in the scrotum.
Undescended Testicle Symptoms
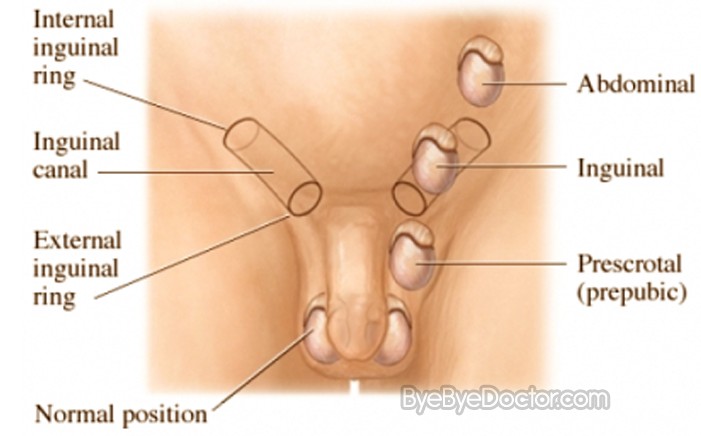
During fetal development, testicles develop in the abdominal area. The last several months of common development of the fetus, the testicles steadily leave the abdomen; pass thru a tubular passage in the area of the groin known as the inguinal canal and drops down into the scrotum sac.
If your baby boy has a testicle which is undescended, that route was delayed or stopped in some stage of growth. So, you will not feel or see a testicle in the area or place you would expect one to be in the scrotum.
Your baby’s doctor will usually detect a testicle which is undescended when the baby is observed after birth. You will need to find out from the physician how frequently your son will need to be examined. Usually if the testicle has not progressed into the scrotum by the age of four months, this problem with your son probably will not correct itself.
If this problem is treated while the boy is still a baby it will help to lower the hazard of any difficulties in the future – problems such as testicular cancer or infertility.
Older boys –from babies to boys who are pre-adolescent—who have testicles which have descended normally at birth can seem to be “missing” a testicle later on. This condition can point to:
- A retractile testicle changes back and forth between the groin and the scrotum and can be easily directed by hand into the scrotum sac during a doctor’s exam.
- An acquired undescended testicle or ascending testicle which has “returned” to the groin and cannot be directed easily manually into the scrotum sac.
If either of these changes is noticed in a boy’s genitals or there is any concern about his growth, a visit to his physician is advisable.
Undescended Testicle Causes
The precise reason for this condition with testicles is not known. It could be a mixture of genetics, health of the mother, and environmental issues which somehow interrupt the hormones, changes physically as well as activity with the nerves can affect the growth of the testicles.
Birth weight which is low as well as early birth are the risk factors which are best understood and which can increase the probability of undescended testicle in a newborn. Additional risk factors are not understood well. Conditions which can escalate the risk include:
http://www.Symptoms-Causes-treatment.blogspot.com detect diseases at an early stage symptoms, and find out the causes and treatments best suited.
- Early birth
- Low birth weight
- Fetus conditions which can restrict growth, such as Down syndrome or abdominal wall deficiency
- History in the family of undescended testicle or other problems with development of the genital
- Mother’s use of alcohol during pregnancy
- Mother’s smoking of cigarette or being exposed to smoke which is secondhand
- Mother is obese
- Mother is diabetic
- Exposure by parents’ to pesticides
In order for testicles to function and develop normally, they must be slightly cooler than the normal temperature of the body. The scrotum offers this cooler setting. Until a boy is three or four years old, the testicles remain experiencing changes that affect how they will function later.
Any undescended testicle is not in a cooler setting. This can escalate the risk of any complications later in life. Common complications include:
- Testicular cancer.
- Problems with fertility.
Undescended Testicle Treatment
A doctor can fairly easily define that a testicle has not moved into the scrotum. The aim of additional examination is to find the location of the testicle and monitor any changes in its position. If the testicle is in the groin, the doctor may have the ability to locate it by touch. If it cannot be felt, the doctor will more than likely refer you to a pediatric urologist for further tests. Some un-dropped testicles are nonpalpable.
Undescended Testicle Surgery
An un-dropped testicle is typically fixed with an operation. The physician cautiously works the testicle into the scrotum sack and sutures it into place. The technique usually entails fairly slight slits and can be done by laparoscopy.
When to schedule the baby’s surgery will be determined by several factors, for instance the boy’s health and how problematic the surgery might be. The surgeon will probably endorse preforming the surgery after the baby is three to six months old and prior to turning 15 months old. Prompt surgical management seems to lessen any threat of future difficulties.
In certain circumstances, the testicle can be poorly formed, atypical or dead tissue. The surgeon will eliminate this testicular matter.
If the baby similarly has an inguinal hernia linked with the undescended testicle, this hernia is mended during the same surgery.
Following surgery, the physician will observe the testicle to make certain that it continues to mature, functions correctly and most of all stays in place. Monitoring/checking may include:
Physical examination
Ultrasound exam of the scrotum
Hormone levels tests
Hormone treatment
Other treatments
If the baby does not have 1 or either testicles – either gone or did not endure after surgery – you can deliberate on “saline testicular implants” for the scrotum that are inserted during early adolescence. These inserts – testicle-shaped nodes filled with a fluid –have the look of 2 testicles in the scrotum sac.
- If the baby does not have as a minimum one fit testicle, the doctor will speak with you about seeing an endocrinologist or hormone specialist to converse about hormone treatments in the future that will be essential to bring about puberty as well as physical maturity.
Undescended Testicle Pictures