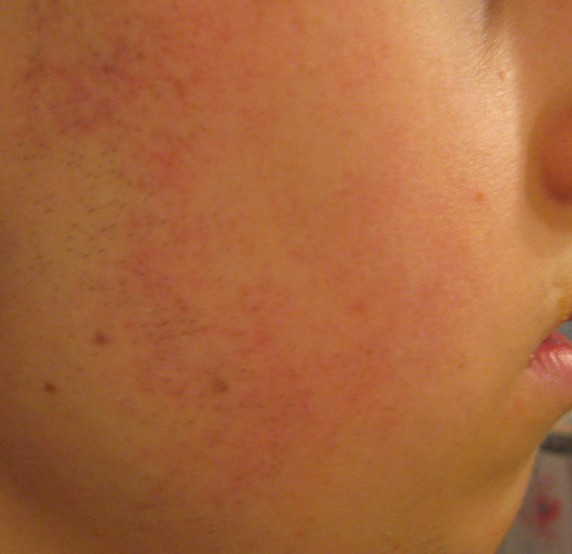
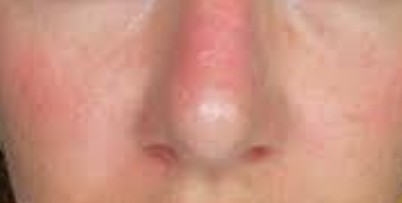
Shingles is a skin rash caused by varicella-zoster virus, a type of herpes virus, which causes a disease known as chickenpox. Shingles is an infection that occurs on the nerve and area of skin, which is supplied with nerve endings. People who have had chickenpox previously can develop shingles rash. Even those who have had mild chickenpox can also suffer from shingles.
Herpes zoster virus is different from herpes simplex because the latter causes genital herpes, which is a different condition from shingles. It is estimated that 1 in 5 people are likely to develop shingles in their life. This condition can occur at any age but it is more susceptible to people over the age of 50. Rarely does shingles rash manifest more than once but about 1 in 50 persons are likely to develop shingles more than once.
Causes
Mainly shingles rash may occur for no obvious reason but at other times, the condition may be caused by stress and illness triggers. The weakened and ageing immune system in older people may be one reason why they develop the rash. The immune system suppresses the virus and keeps it inactive thus preventing it from multiplying. Therefore, if there is slight weakened immune system, as it happens in older people, the virus may reactivate and multiply leading to development of shingles.
Many people suffer from chickenpox at their childhood stage. When a child or a person suffers from chickenpox, the virus that causes this condition does not completely disappear and it remains dormant in body. Some virus particles remain in the nerve roots surrounding the spinal cord in an inactive state. When these particles are present in nerve roots, they do not cause harm there since they are inactive. They do not show symptoms.
However, for reasons not clearly understood, these inactive virus particles may start multiplying or reactivating after some years of dormancy. When the virus is reactivated at the spinal cord nerve area, it travels along the nerve to the reach the skin where it causes shingles. Shingles is more prevalent in people with immunosuppressant or poor immune system.
Young people with HIV and AIDS may suffer the condition. Similarly, people who have suppressed immune system as a result of use of treatment options like chemotherapy and steroids may also suffer from the condition. Being exposed to shingles may not cause the rash but if you get in contact with a person with shingles and you have not suffered from chickenpox before or you have not received chickenpox vaccine, there is possibility of suffering from chickenpox.
You can be exposed to chickenpox if you come in contact with fluid from the shingles blisters.
Being over 50 years places you in a high risk of suffering from shingles. If you have recently had a surgery or you have been using cancer treatment medication like chemotherapy, then you may be susceptible to suffering shingles. Other risk factors include radiation therapy, AIDs, cancer, poor nutrition, stress, organ transplant, diabetes, and lupus, which suppress the immune system.
Symptoms of shingles rash
The varicella-zoster virus mainly affects one nerve and on one side of the body. The skin area supplied with nerves begins showing symptoms like pain and rash. At times, two or more nerves that are close to one another are affected by the virus. The mainly nerves affected are those which reach the skin on abdomen, chest, upper face, and the eyes.
Early symptoms of the condition include sensitivity to light, headache, and flu-like symptoms with no fever. The itching and tingling begin on the band of skin. A person with the condition has a localized band of pain. The pain can occur anywhere and it depends on which nerve is affected. The pain also ranges from moderate to severe. The pain may be constantly dull or at times, it may be gnawing pain. At other times, you may experience sharp and stabbing pain, which comes and goes.
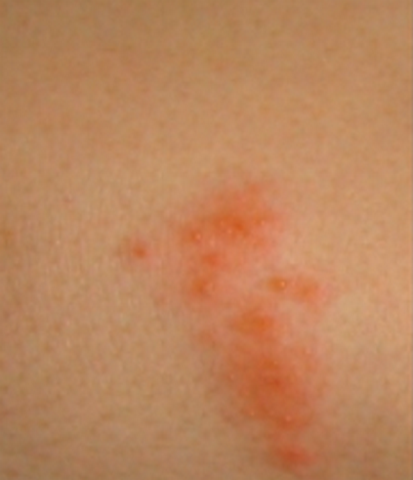
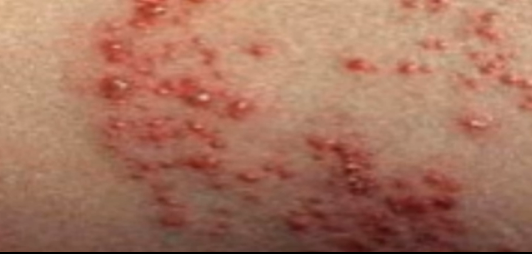
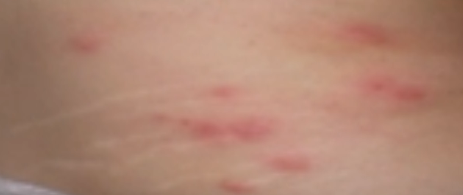
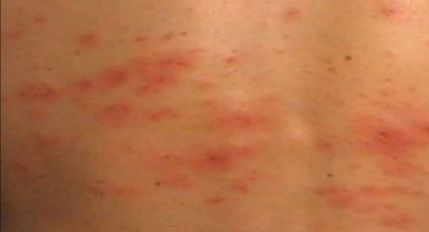
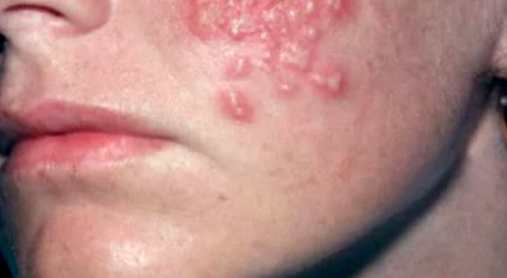
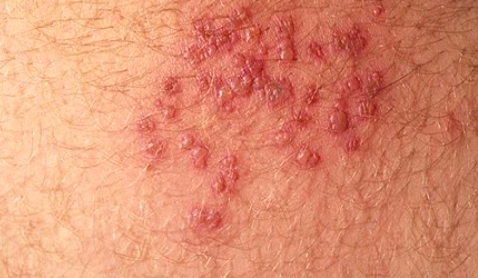
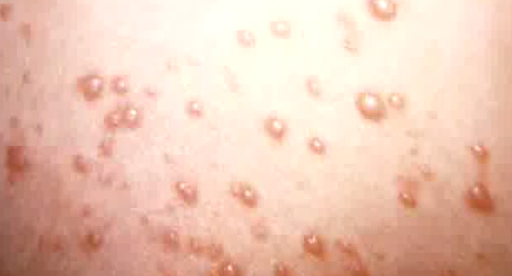
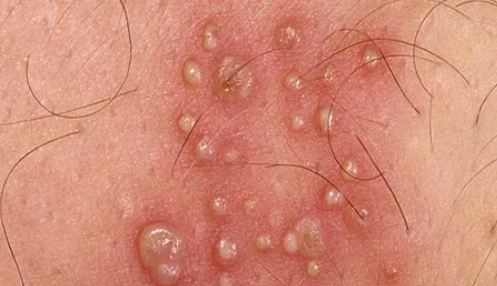
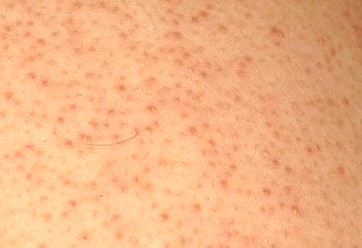
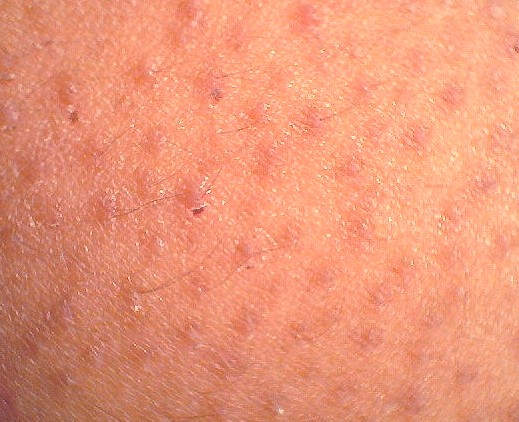
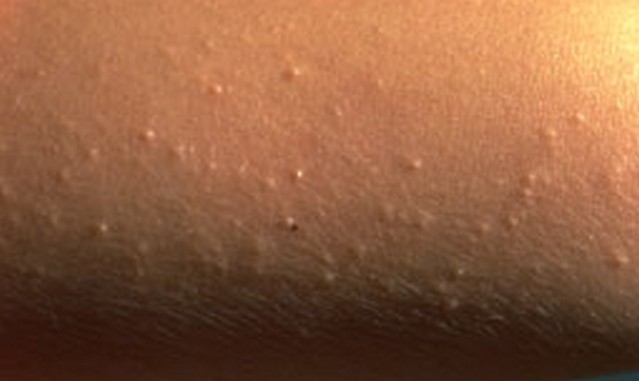
The affected skin becomes tender. A rash occurs within 2 to 3 days following the start of pain. First, red blotches appear and they develop into itching blisters. The rash appears like chickenpox but it only affects the area of the band of skin, which hosts the affected nerves. The tissue under and around the rash may become inflamed due to effects of the virus attack. The blisters dry and form scabs before they eventually fade away. The area where the blisters occurred may have slight scarring.
Treatment
There is no cure for this skin condition but there are treatments, which can shorten the illness and prevent other health complications from occurring. Antiviral medicines are introduced to help relieve pain and shorten the duration of the shingles rash. To relieve pain, antidepressants and topical creams are applied. When treatment with antiviral is given in advance, it can help prevent later complications like postherpetic neuralgia. Antibiotics are used to stop infection of blisters.
Shingles Rash Pictures